Articles
The Litchfield pluton in south-central Maine:
Carboniferous alkalic magmatism in northern New England, USA
ABSTRACT
The Litchfield pluton is a poorly exposed 7 km2 composite alkalic intrusive complex that cuts previously deformed and metamorphosed Silurian turbidites in south-central Maine. The pluton includes a variety of alkaline syenites, including the type locality of “litchfieldite,” a coarse-grained cancrinite-, sodalite-, and lepidomelane-bearing nepheline syenite first recognized over 150 years ago and common in many petrologic collections. A new U-Pb zircon age of 321 ± 2 Ma from the nepheline syenite is interpreted to represent the crystallization age of the plutonic complex. A new biotite 40Ar/39Ar age of 239 ± 1 Ma from the syenite is similar to previously published mica ages from the surrounding country rocks and dates the time of regional cooling in the area below ~ 300°C. Whole-rock chemical analyses of rocks of the Litchfield pluton reveal silica-undersaturated alkaline compositions that are consistent with formation in a within-plate tectonic setting. The age and geochemical characteristics of the alkalic igneous rocks near Litchfield are consistent with a model that invokes the generation of a small volume of alkalic magma beneath south-central Maine during a period of Carboniferous transcurrent tectonism in the northern Appalachian orogen.
RÉSUMÉ
Le pluton de Litchfield est un complexe intrusif alcalin composite de sept kilomètres carrés peu affleurant qui recoupe des turbidites siluriennes précédemment déformées et métamorphisées dans le centre-sud du Maine. Le pluton inclut diverses syénites alcalines, notamment la localité type de la « litchfieldite », une syénite néphélinique renfermant de la cancrinite, de la sodalite et de la lépidomélane à grain grossier identifiée pour la première fois il y a plus de 150 ans et répandue dans maintes collections pétrologiques. Une nouvelle datation U-Pb sur zircon de 321 ± 2 Ma de la syénite néphélinique est interprétée comme une représentation de l’âge de la cristallisation du complexe de roches plutoniques. Une nouvelle datation de la syénite par biotite et 40Ar/39Ar de 239 ± 1 Ma est similaire aux âges du mica des roches encaissantes voisines publiés auparavant et situe le moment du refroidissement régional dans le secteur au-dessous d’environ 300 °C. Des analyses chimiques sur roche totale des roches du pluton de Litchfield révèlent des compositions alcalines sous-saturées de silice correspondant à une formation dans un milieu tectonique intraplaque. L’âge et les caractéristiques géochimiques des roches ignées alcalines près de Litchfield sont conformes à un modèle évoquant la production d’un volume modeste de magma alcalin sous le centre-sud du Maine durant une période d’activité tectonique de coulissage du Carbonifère dans le nord de l’orogène appalachien.
[Traduit par la redaction]
INTRODUCTION
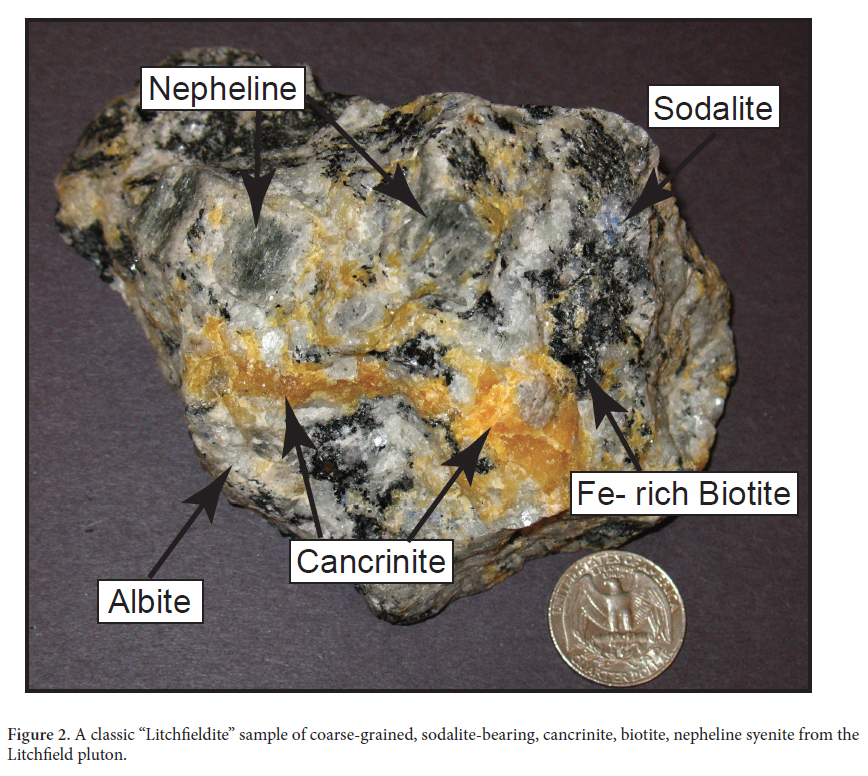
1 Since the mid-1800s (Jackson 1845; Clarke 1886), the small village of Litchfield in south-central Maine (Fig. 1) has been known as a collecting locality for specimens of cancrinite, sodalite, nepheline, and lepidomelane (Fe-rich biotite). The host rock to these minerals, a coarse-grained nepheline syenite (Fig. 2) that was assigned the name “litchfieldite” by Bayley (1892), is part of a composite alkalic plutonic complex (Barker 1965) that occupies an area of approximately 7 km2 (Fig. 3). While these unusual rocks have attracted the interest of mineral collectors for over a century and a half, extremely poor exposure has discouraged detailed study; thus the age and tectonic significance of these unusual rocks have remained elusive.
 Display large image of Figure 1
Display large image of Figure 1
 Display large image of Figure 2
Display large image of Figure 2
 Display large image of Figure 3
Display large image of Figure 3
2 Silica-undersaturated, nepheline-bearing plutonic rocks are uncommon in the geological record and are generally attributed to small degrees of partial melting of previously metasomatized mantle in anorogenic tectonic settings (e.g., Woolley 2001; Martin et al. 2012). Burke et al. (2003) have also proposed that the presence of these alkaline plutonic rocks may be indicators of ancient suture zones. Detailed studies of these unusual rock types, when they are present, can thus be used to provide important constraints on the tectonic setting of a region at the time of their formation. Additionally, these rocks have received renewed attention due to their tendency to contain relatively high abundances of rare earth and high field strength elements (Kogarko 1990; Sørensen 1992; Möller and Williams-Jones 2016).
3 In the last detailed study completed on alkaline rocks of the Litchfield pluton, Barker (1965) suggested that they are associated with the Mesozoic White Mountain magma series. However, limited major element geochemical data are available from these rocks, and no isotopic igneous crystallization ages have been published. The purpose of this paper is to report new U-Pb zircon ages and complete whole-rock chemical analyses from a limited number of samples of the Litchfield pluton in south-central Maine. These data are then used to determine the igneous crystallization age of the pluton and speculate on the processes responsible for the generation of this unusual magma composition. Additionally, the new age constraints provided by our U-Pb work allow us to make connections with other alkaline igneous rocks of broadly similar age in the northern Appalachian orogen and place constraints on the tectonic setting of the region at the time of intrusion.
GEOLOGICAL SETTING
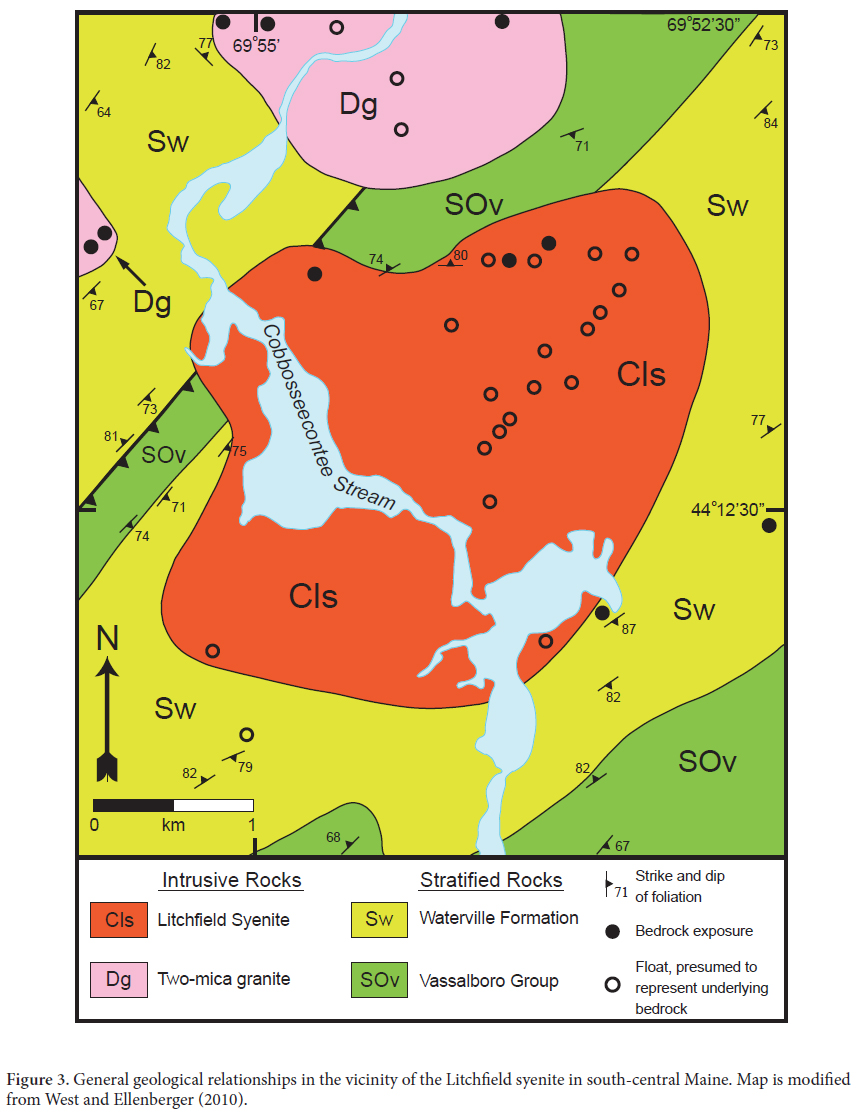
4 The Litchfield pluton occupies a topographic basin in an area of very poor bedrock exposure. Although these unusual rocks had been the subject of directed mineralogical studies since the late 19th century (Clarke 1886; Bayley 1892), field relationships were first mapped in detail by Barker (1965), and more recently at a scale of 1:24 000 by West and Ellenberger (2010). Bedrock outcrops are most abundant in the northern part of the pluton, but the map pattern of the pluton is based primarily on the spatial distribution of alkalic granitoid boulders. Although contacts between the plutonic rocks of the Litchfield pluton and the surrounding country rocks are not exposed, map patterns in the surrounding country rocks appear to be truncated by the inferred outline of the pluton (Barker 1965; West and Ellenberger 2010).
5 Hence the Litchfield pluton is interpreted to intrude Late Ordovician (?) to Silurian metamorphosed turbidites (mostly thin-bedded schist, granofels, quartzite, and more rarely impure carbonate rocks) of the Central Maine Sequence (Osberg 1988; Marvinney et al. 2010). These country rocks were multiply deformed and metamorphosed to amphibolite-facies conditions during the late Silurian-Early Devonian Acadian orogeny (Gerbi and West 2007). While many of the alkalic rocks of the Litchfield pluton show weak to moderate preferred orientation of dark colored minerals, thin sections reveal little to no evidence for significant penetrative deformation or metamorphic recrystallization. Additionally, Barker (1965) reported that foliation in the plutonic rocks is locally at right angles to the foliation in adjacent metasedimentary rocks. Thus, while contacts cannot be observed directly, field relationships indicate the intrusion post-dated regional deformation and metamorphism associated with the Acadian orogeny.
6 In the general area of the Litchfield pluton, constraints on the timing of amphibolite-facies metamorphism are provided by a U-Pb age of 381 ± 4 Ma on metamorphic zircon overgrowths in the Hornbeam Hill pluton located approximately 15 km south of the present study area (West and Cubley 2006; Gerbi and West 2007). A 40Ar/39Ar hornblende cooling age of 349 ± 5 Ma from country rocks exposed approximately 10 km east of the Litchfield pluton indicates the time of regional cooling below approximately 500°C following this metamorphism (West et al. 1988). Finally, a large number of 40Ar/39Ar biotite ages from both plutons and country rocks in the immediate area constrain the time of regional cooling below approximately 300°C in the vicinity of the Litchfield pluton to have occurred approximately 240 to 250 million years ago (Dallmeyer 1979; 1989). Dallmeyer (1989, p. 427) reported that “Dallmeyer (1979) presented a 227 ± 5 Ma 40Ar/39Ar plateau age for biotite from nepheline syenite” near Litchfield, Maine. However, a review of Dallmeyer (1979) did not reveal these data.
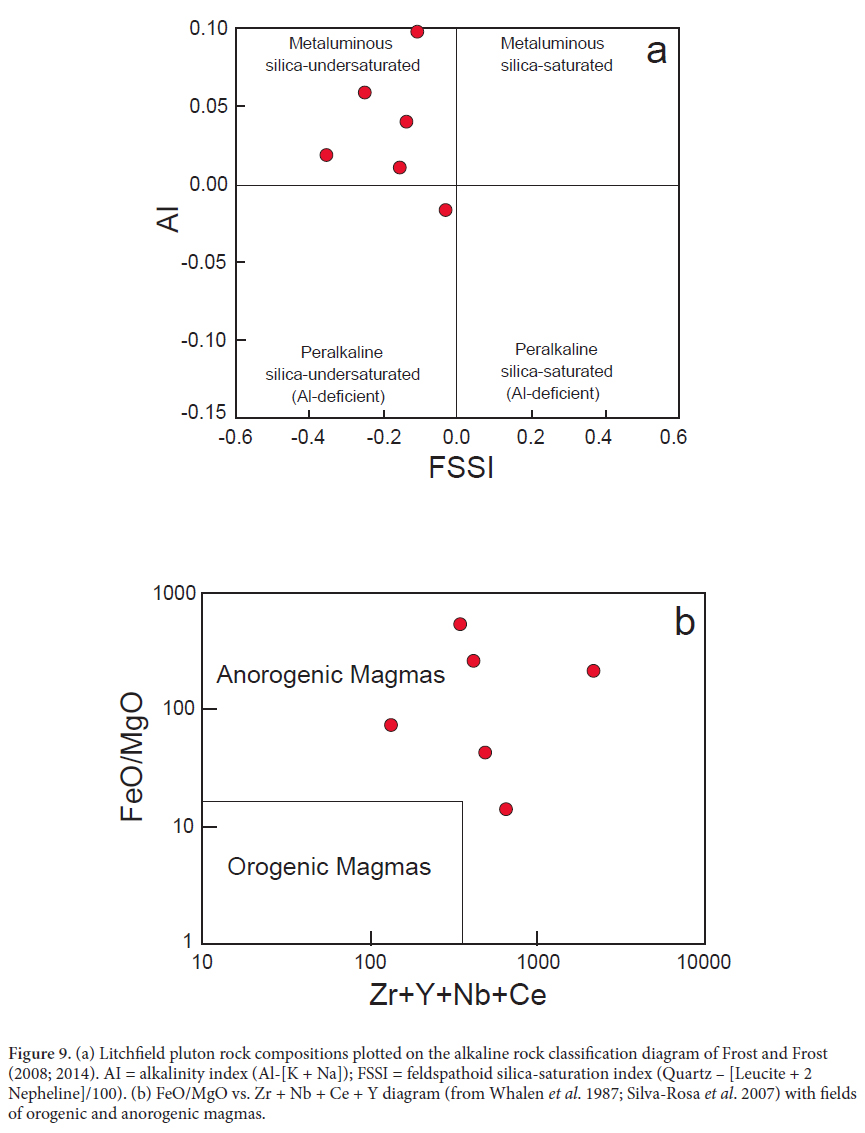
PREVIOUS WORK
7 Although the unusual rocks near Litchfield, Maine, had been known to mineral collectors for decades prior, Clarke (1886) provided the first detailed mineralogical descriptions of nepheline syenite from the Litchfield pluton. This work included major element mineral chemistry for cancrinite, nepheline, and biotite from these rocks. Of note, Clark (1886) showed that biotite in this rock, long referred to as “lepidomelane,” is high in both Fe2O3 (19.49 wt.%) and FeO (14.10 wt.%), low in MgO (1.01 wt.%), and completely lacking in TiO2. While no detailed mineral chemistry is presented here, analysis of biotite using energy dispersive spectrometry on a scanning electron microscope confirmed that biotite from these rocks is high in iron and contains virtually no titanium or magnesium.
8 Bayley (1892) provided the first whole-rock chemical analysis (major elements only) from nepheline syenite of the Litchfield pluton and these old results are consistent with the modern results presented later in this paper. Upon review of the unusual aspects of the cancrinite-bearing nepheline syenite, Bayley (1892, p. 243) reported: “Its peculiarities are so strongly marked that the rock seems worthy of a distinctive varietal name, for which no more appropriate one can be found than litchfieldite, derived from the familiar locality – Litchfield – whence nearly all the specimens were obtained.” The rock name “litchfieldite” is included in the most recent IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Igneous rocks (Le Maitre et al. 2002, p. 105) and is therein defined as “a coarse-grained, somewhat foliated variety of nepheline syenite consisting of K-feldspar, albite, nepheline, cancrinite, sodalite and lepiodomelane.”
9 Daly (1918) published the first systematic field descriptions of rocks associated with the Litchfield pluton, and was the first to describe other alkalic plutonic rocks in the area (e.g., nepheline-deficient, amphibole-bearing syenite). No detailed petrologic descriptions, geochemical data, or geologic map accompanied this work. Daly (1918, p. 469), based upon this limited field-based investigation, concluded that “ . . . it is tolerably certain that there is no large mass of litchfieldite in the region. The celebrated boulders seem to have been derived from short, sill-like pods injected into the prevailing crystalline schists.” Additionally, Daly (1918) concluded that the unusual alkaline rocks were formed through variable assimilation of limestone in granite magma.
10 In the nearly 100 years since the publication of Daly’s work, only the detailed field and petrologic study of Barker (1965) and bedrock mapping of West and Ellenberger (2010) have provided additional data on the alkalic plutonic rocks near Litchfield, Maine. Barker’s study revealed three main rock types within what he interpreted to be a composite pluton: (1) fine-grained, leucocratic syenite that contains limited amounts of Na-rich pyroxene (aegirineaugite) and amphibole (riebeckite-arfvedsonite) with no nepheline or quartz; (2) medium- to coarse- grained, magnetite-bearing biotite syenite that similarly contains no nepheline or quartz; and (3) coarse-grained, foliated, biotite nepheline syenite that includes the “type variety” of litchfieldite described by Bayley (1892) and the rock type that is found in most petrologic collections (shown in Figure 2). Barker (1965) also recognized rare cross-cutting dykes of mafic syenite and albite-rich pegmatite, but these rocks types could not be located in the field during the present study.
11 Barker (1965) interpreted the three main alkalic rock types described above to be included within a single oval-shaped composite pluton occupying an area of approximately 7 km2. Although West and Ellenberger’s (2010) later detailed mapping recognized Barker’s (1965) three main alkalic rock types in the field and confirmed an overall map pattern consistent with that portrayed in Barker (1965), they did not subdivide the pluton into different phases due to the limited availability of in situ outcrops. Barker (1965) interpreted the different alkalic rock types in the Litchfield pluton to have been produced by differentiation of an initial nepheline syenite magma; furthermore, he suggested that, in places, country rock assimilation and metasomatism resulted in the late-stage textural and mineralogical variety observed within individual phases. Finally, Barker (1965) correlated rocks of the Litchfield pluton with three other nepheline syenite occurrences in New England that are now known to be Mesozoic in age (i.e., Cuttingsville, Vermont: 100 Ma, Armstrong and Stump 1971; Red Hill, New Hampshire: 194 Ma, Foland and Faul 1977; and Pleasant Mountain, Maine: 112 Ma Foland and Faul, 1977).
PETROGRAPHY
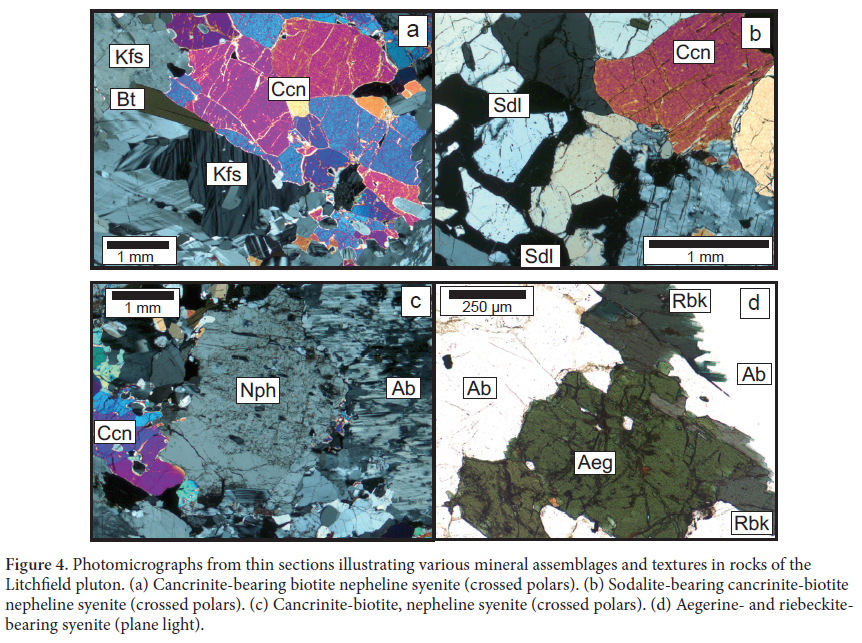
12 As discussed in all previous studies, the paucity of fresh in situ exposures greatly hinders detailed petrologic study of the Litchfield alkalic rocks. Despite this, representative samples of each of the three major rock types identified by Barker (1965) and confirmed in this study were collected. Bayley (1892) provided detailed petrographic descriptions of the litchfieldite, and Barker (1965) provided multiple modal analyses of each of the rock types within the pluton and the reader is referred to these works for details. The type “litchfieldite” (Fig. 2) is coarse-grained and rich in K-feldspar and albite (combined about 70%); it contains conspicuous yellow granular-textured cancrinite, greasy-grey coarse-grained nepheline, and less common fine-grained blue sodalite. Accessory minerals include coarse-grained biotite that is typically segregated into streaks within the lighter colored minerals, and euhedral zircon prisms up to 5 mm in length. Representative photomicrographs of litchfieldite are shown in Figures 4a-c. Nepheline comprises up to 20% of the rock and forms subhedral to anhedral grains up to 3 cm across. Based upon old chemical analyses (Clark 1886; Barker 1965), the nepheline has a compositional range of Ne 70-80 . Cancrinite is anhedral, occurs in abundances of up to 10%, and shows no apparent textural affinity for other minerals. Sodalite is fine grained (< 3 mm) and occurs in abundances of less than 1%.
 Display large image of Figure 4
Display large image of Figure 4
13 Fine-grained, nepheline- and cancrinite-absent syenite is most commonly found in the northern part of the pluton and is characterized by accessory Na-rich amphibole and pyroxene (Fig. 4d). These rocks are notably leucrocratic (color index <5) with the sizes of individual minerals rarely exceeding 5 mm across. Finally, coarse-grained nephelineand cancrinite-absent biotite syenite (± magnetite) that texturally appears similar to the litchfieldite occurs in the central and southern portions of the pluton.
ANALYTICAL METHODS
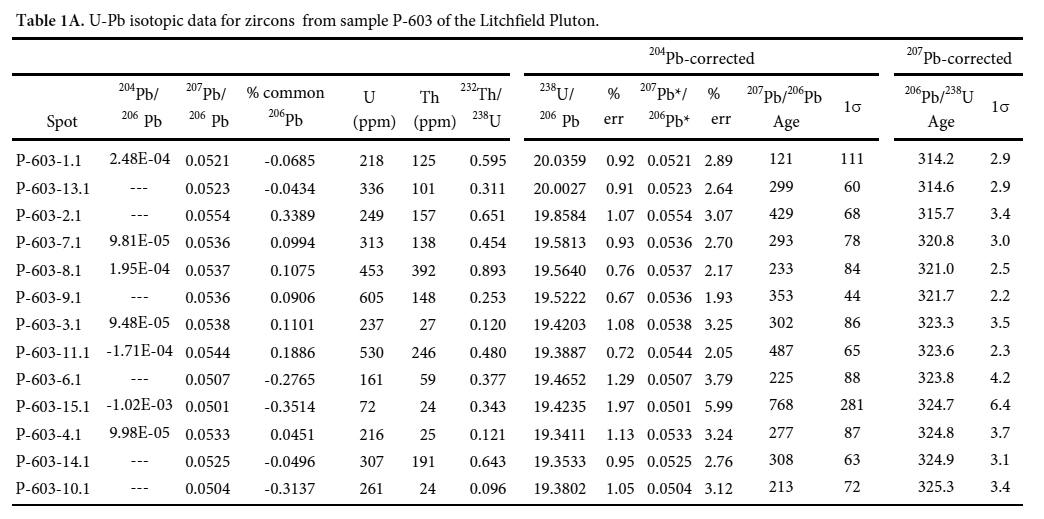
14 Elongate, prismatic, and clear zircons displaying igneous zoning were separated from a sample of cancrinite-bearing nepheline syenite (P-603) from the Litchfield pluton. U-Pb isotopic analyses were carried out on these zircons at the United States Geological Survey-Stanford University sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe (SHRIMP) during a session in March of 2011. Bradley et al. (2014) described analytical techniques used at this lab. A total of 13 spot analyses were completed and all individual spot results are reported in Table 1 and shown on Figure 5 as 206Pb/238U ages with 1 sigma uncertainty.
 Display large image of Table 1
Display large image of Table 1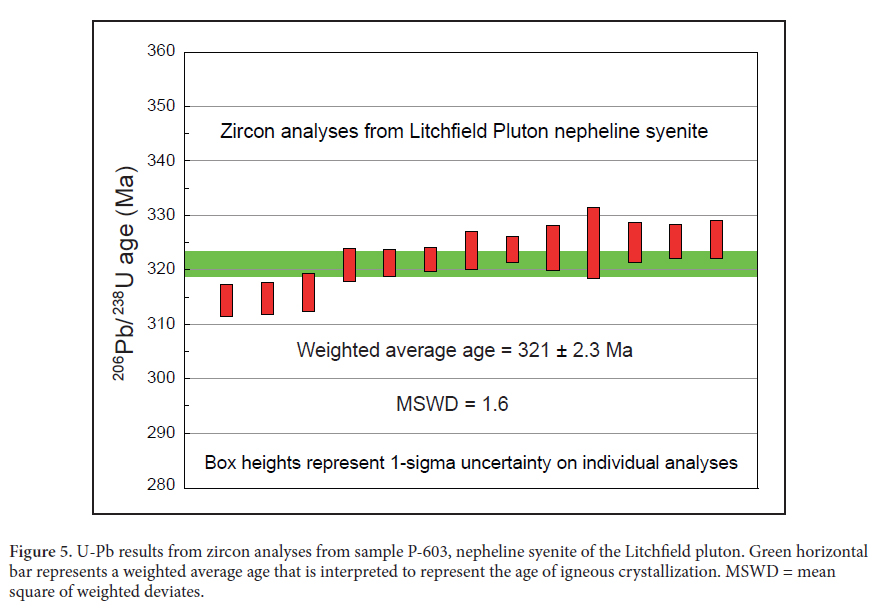 Display large image of Figure 5
Display large image of Figure 5
15 Biotite was also separated from sample P-603 and it was analyzed by the 40Ar/39Ar technique as a single total fusion increment. The sample was encapsulated and irradiated in the United States Geological Survey TIRGA reactor in Denver, Colorado (Dalrymple et al. 1981) with the MMhbhornblende age standard (Alexander et al. 1978; 519.4 ± 2.5 Ma) used as a flux monitor. The sample and flux monitors were analyzed at the United States Geological Survey argon dating laboratory in Reston, Virginia, and the details of analytical methods employed are discussed in Kunk et al. (2005). Decay constants were those recommended by Steiger and Jäger (1977). The analytical results of this experiment are shown in Table 2 and the total fusion age is reported with two-sigma uncertainty.
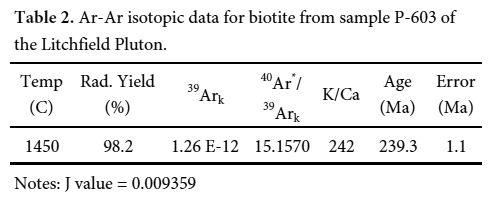 Display large image of Table 2Notes: J value = 0.009359
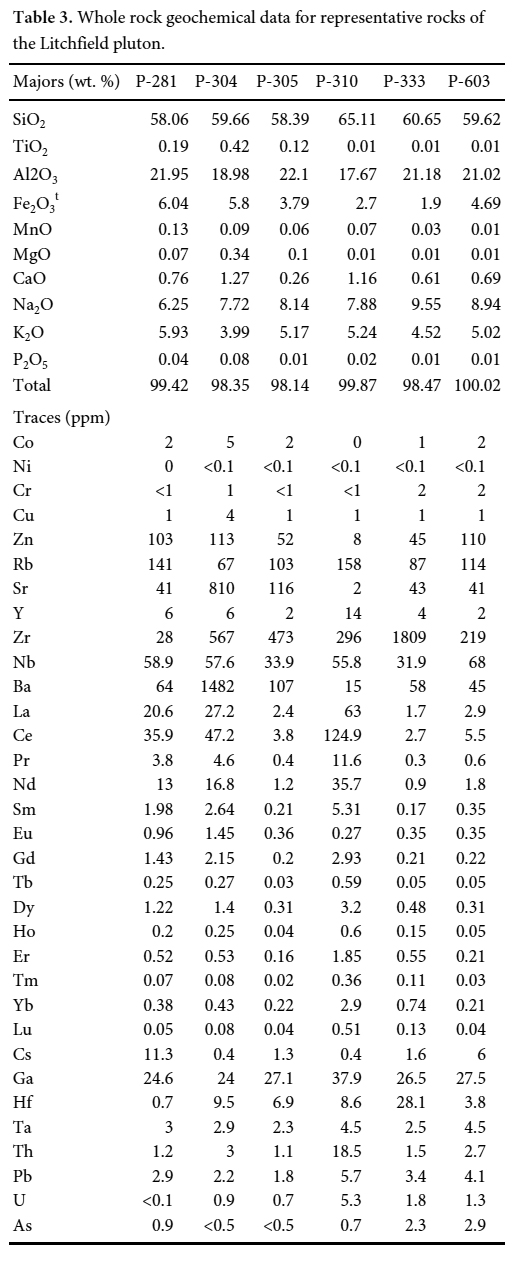
Display large image of Table 2Notes: J value = 0.009359 16 Six samples representing a range of bulk compositions identified through field and petrographic observations were selected for whole-rock chemical analysis (locations and brief hand sample descriptions are provided in Appendix A). These samples were crushed in a porcelain jaw crusher and powdered in a tungsten carbide shatterbox. We recognize that the use of tungsten carbide has the potential to introduce small amounts of tantalum contamination; however, we do not consider this to be significant in this study given the relatively high concentrations of tantalum in the samples analyzed. A full suite of major- and trace-element analyses (Table 3) was completed at Acme Analytical Laboratories Ltd. in Vancouver, British Columbia. Major elements were measured using ICP-emission spectrometry and trace elements were measured using ICP-mass spectrometry. Both methods used lithium metaborate fusion techniques to prepare the samples for ICP analysis.
 Display large image of Table 3
Display large image of Table 3GEOCHRONOLOGY
U-Pb data
17 Thirteen new SHRIMP U-Pb zircon ages from a single sample of cancrinite-bearing nepheline syenite are presented in Table 1 and shown graphically in Figure 5 (sample P-603: see Appendix A for location and a general rock description). The zircons analyzed are colorless and cathodoluminescence images (not shown) reveal zoning patterns consistent with igneous crystallization. Individual zircon ages are concordant within analytical uncertainties, and 206Pb/238U ages range from 314.2 to 325.3 Ma. A weighted average of the thirteen 206Pb/238U spot ages is 321.1 ± 2.3 Ma (2σ) (MSWD = 1.6) and we interpret this age to represent the age of igneous crystallization of the nepheline syenite.
40Ar/39Ar data
18 The results of a biotite total fusion 40Ar/39Ar analysis are presented in Table 2. The sample was analyzed as a single total fusion step rather than step-heated because it has been established that biotite release spectra do not reveal reliable information about the internal distribution of argon within the sample (McDougall and Harrison 1999). The total fusion age of 239.3 ± 1.1 Ma (2σ) determined from this sample is interpreted to represent the time of post-crystallization cooling of the Litchfield pluton below the closure temperature of biotite (~ 300°C: McDougall and Harrison 1999).
GEOCHEMISTRY
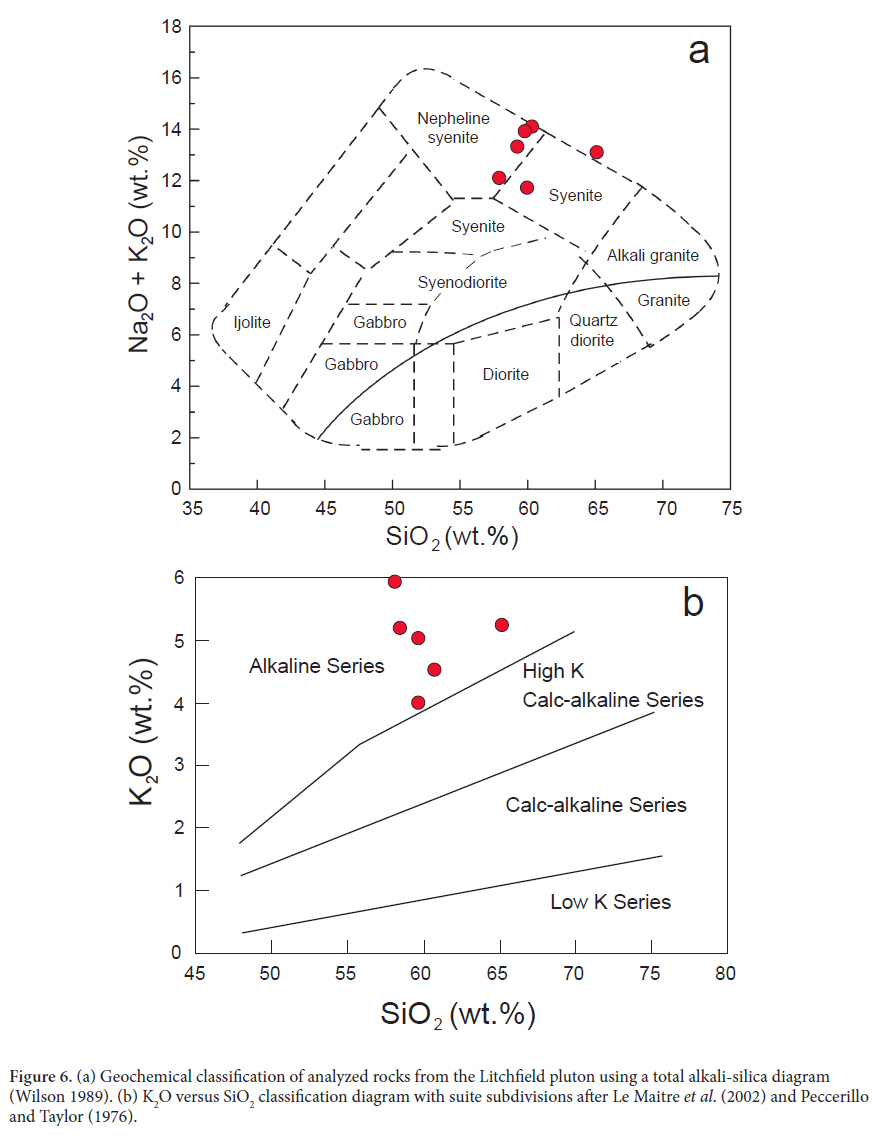
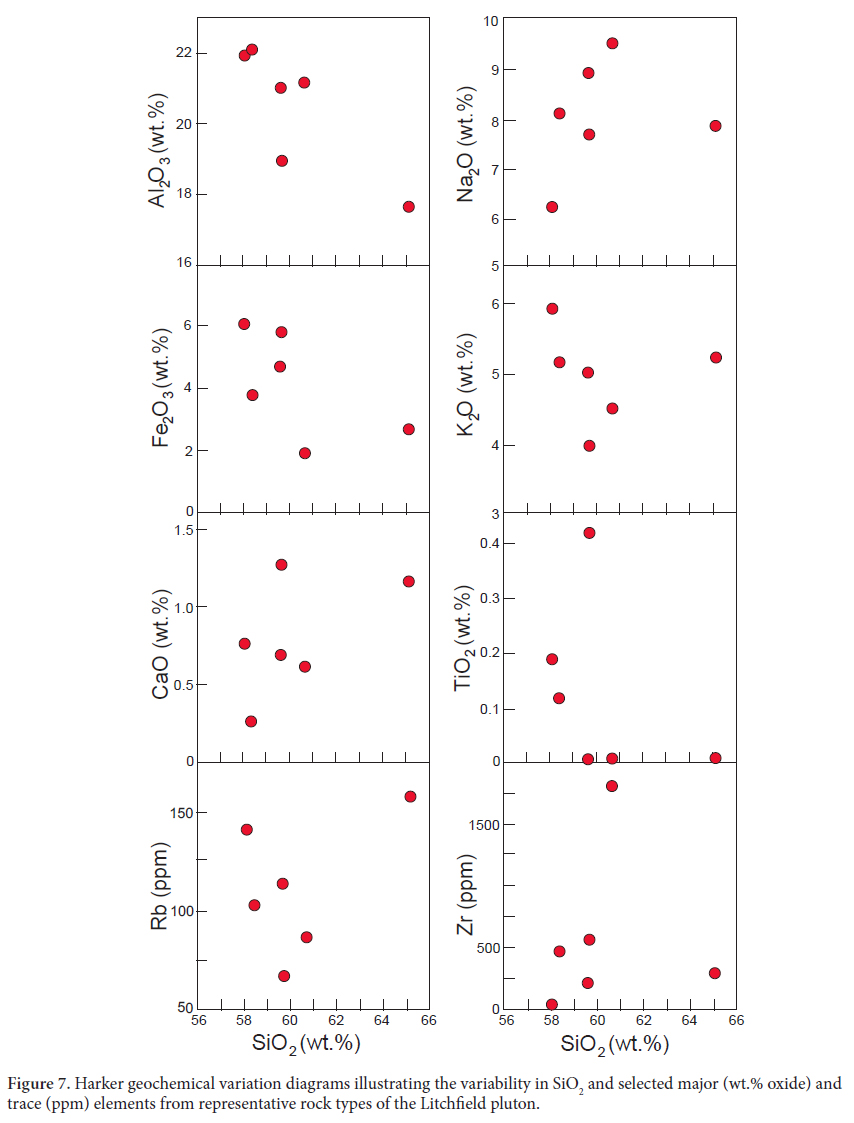
19 The whole rock major and trace element compositions of representative samples of the Litchfield pluton are presented in Table 3. The rocks are intermediate in terms of their SiO2 contents (58 to 65 wt.%) and all contain high concentrations of both K2O (4 to 6 wt.%) and Na2O (6 to 9.5 wt.%). The rocks are also notably depleted in MgO (5 of 6 samples ≤0.1 wt. %), and also have low concentrations of TiO2 (5 of 6 below 0.2 wt.%) and CaO (0.26 to 1.27 wt.%). On a total alkali versus silica diagram (Fig. 6a) the rocks are classified as nepheline syenite and syenite, and on a SiO2 versus K2O diagram, compositions plot in the alkaline field (Fig. 6b). All of the samples analyzed are nepheline normative (range = 1.0 to 17.5% normative nepheline). Although there is variability in the major element abundances between the different rock types, Harker diagrams (Fig. 7) reveal no discernable fractionation trends.
 Display large image of Figure 6
Display large image of Figure 6
 Display large image of Figure 7
Display large image of Figure 7
20 In terms of trace elements, the rocks are generally characterized by relatively high concentrations of Rb (67 to 158 ppm), Nb (32 to 68 ppm), and Ga (24 to 38 ppm), and highly variable contents of Zr (28 to1809 ppm), Sr (2 to 810 ppm), and Ba (15 to 1482 ppm). All samples are essentially devoid of trace elements compatible with mafic silicates (e.g., Cr and Ni ≤ 2 ppm). As with the major elements, Harker diagrams of trace elements (Fig. 7) reveal no discernable fractionation trends.
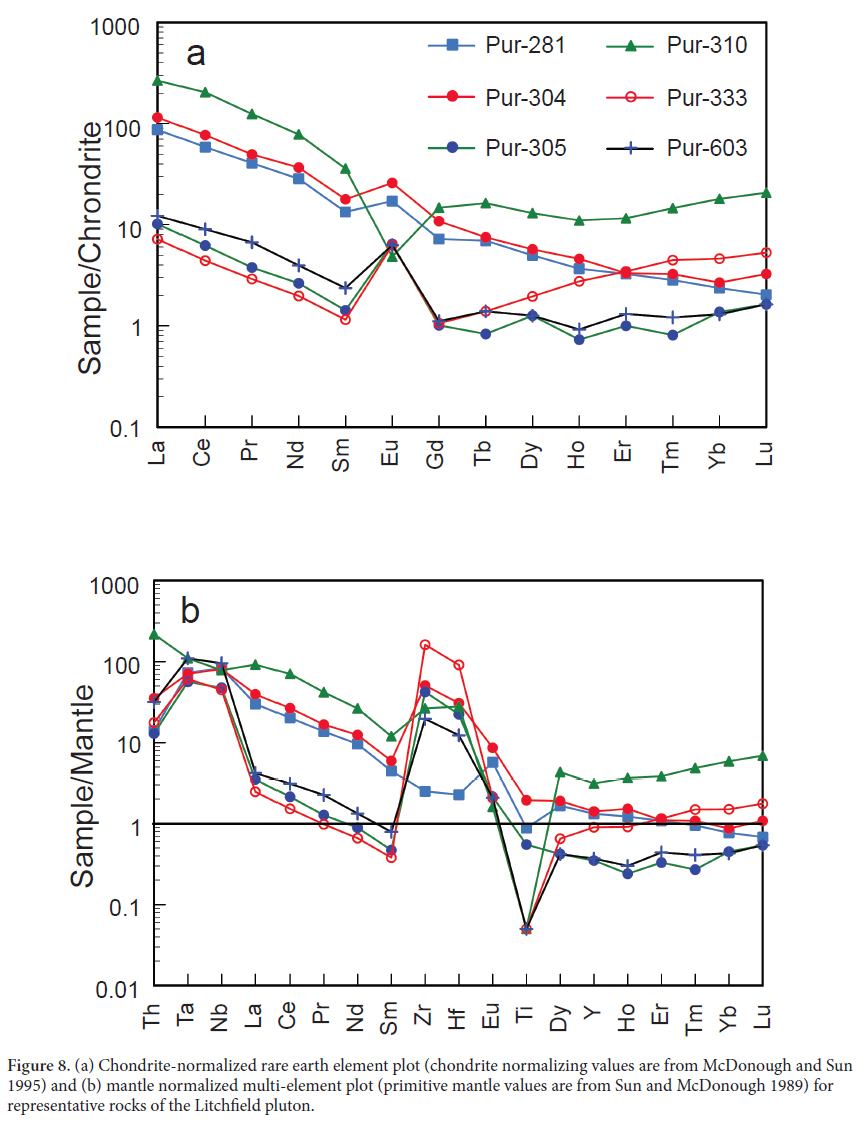
21 A plot of chondrite-normalized rare earth elements (REE) (Fig. 8a) reveals two groupings: one group (n = 3) with significant light REE (LREE) enrichment (~ 90 to 200 times chondrite abundance), and another group (n = 3) with a much less pronounced LREE enrichment (~ 7 to 10 times chondrite abundance). Five of the six samples display a positive Eu anomaly with only the aegerine-riebeckitebearing syenite sample displaying a negative anomaly. The largest positive Eu anomalies are in samples with the lowest total rare earth element contents. The samples have similar primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (Fig. 8b) with most samples showing notable enrichment in Ta, Nb, Zr, and Hf, and all have a negative Ti anomaly.
 Display large image of Figure 8
Display large image of Figure 8
DISCUSSION
Petrogenesis
22 Frost and Frost (2008) devised a means of classifying alkaline igneous rocks and comparing their geochemistry with “normal” granitic rocks based a plot of alkalinity index (AI) versus feldspathoid silica saturation index (FSSI) (refer to Fig. 9a). Syenites of the Litchfield pluton are all silicaundersaturated (FSSI < 0), but there is significant variability in terms of their alkalinity (AI = -0.02 to 0.1), although most of this variability is within the metaluminous field. This pattern of alkalinity can be explained by increasing amounts of plagioclase feldspar fractionation in an alkali basalt parent magma (Frost and Frost 2008; Estrade et al. 2014). Specifically, initial crystallization of calcic plagioclase consumes abundant aluminum, but little sodium and potassium (i.e. the “plagioclase effect” of Bowen 1945). Overall light REE enrichment and relatively flat heavy REE abundances relative to chondrites in the Litchfield pluton (Fig. 8a) are consistent with the geochemistry of most silica-undersaturated igneous rocks (Eby 1990; Woolley 2001).
 Display large image of Figure 9
Display large image of Figure 9
23 In summary, the mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the Litchfield pluton samples analyzed in this study are most consistent with fractional crystallization of an alkalic basaltic parent magma generated through small degrees of partial melting in a within-plate tectonic setting. The variability observed within the pluton itself could be the result of variable amounts of crustal assimilation during the basaltic magma fractionation. Alternatively, some of the variation may be due to sampling both layered and massive parts of the intrusive complex. The samples with low REE abundances and positive Eu anomalies are consistent with accumulation of plagioclase (and perhaps other minerals). Europium substitutes in the calcium sites of plagioclase and thus is used as a measure of plagioclase abundance (e.g., Drake et al. 1975). Samples lacking positive europium anomalies may be from massive units that represent true magma compositions.
24 The association of silica-undersaturated alkaline plutonic rocks with intra-continental tectonic settings is well established (see Woolley 2001 for a summary). The Litchfield pluton is not likely an exception as trace element compositions are consistent with formation in an anorogenic tectonic setting (Fig. 9b). Additionally, Litchfield pluton compositions plotted on various tectonic discrimination diagrams used for quartz-bearing granitic rocks consistently reveal within-plate tectonic settings (e.g., the Rb vs. Y + Nb diagram of Pearce 1996, not shown). It has been shown that anorogenic alkalic magmatism is common in terranes that have recently experienced an episode of collisional tectonics and thus mark times of tectonic relaxation (Martin et al. 2012). This tectonic scenario would fit well with that of south-central Maine in the Carboniferous as the peak period of collisional tectonism in the region (the Acadian orogeny) preceded the intrusion of the Litchfield pluton by about 50 million years (Bradley et al. 2000).
Age correlations
25 Silica-undersaturated alkalic magma of the Litchfield pluton intruded previously deformed and metamorphosed Late Ordovician (?) to Silurian turbidites in south-central Maine at 321 ± 2 Ma. This represents a time when New England was otherwise magmatically quiescent (Bradley et al. 2015a), with the only other known intrusion of similar age being the Palermo pegmatite in central New Hampshire (ca. 326 Ma, U-Pb zircon; Bradley et al. 2015b). Similarly, magmatism in adjacent Atlantic Canada seems to have also been limited during this time span with a notable exception being ca. 335 Ma peralkaline felsic volcanic rocks in the Cumberland Hill Formation in central New Brunswick (Gray et al. 2010; see Fig. 1 for location).
26 Although appreciably older than our reported age for the Litchfield pluton, there does appear to have been a significant pulse of alkalic magmatism in the northern Appalachians in Late Devonian to early Carboniferous time. This includes a suite of ca. 365–355 Ma bimodal intrusive and extrusive alkalic igneous rocks in the Cobequid Highlands of central Nova Scotia (Dunning et al. 2002; Koukouvelas et al. 2002; Pe-Piper and Piper 2002), recently recognized ca. 360–345 Ma alkalic igneous rocks of the Partridge Island Block in southern New Brunswick (Park et al. 2014), and a suite of ca. 373 Ma bimodal alkalic volcanic rocks in the Narragansett Basin of southern New England (Maria and Hermes 2001; Thompson and Hermes 2003).
27 Correlating the age of the Litchfield pluton to stratigraphic sequences in the northern Appalachians is aided by recent improvements in the geologic time scale. Calibrated to the time scale of Gradstein et al. (2012), the Litchfield pluton was emplaced during the first half of the Bashkirian (323.2–315.2 Ma; early Pennsylvanian). This time span equates to the latter part of the Namurian of western Europe and Eastern Canada, and to the Morrowan of the United States (Gradstein et al. 2012). There are no stratified rocks of this age in Maine, the closest being probable Mississippian red beds found in narrow fault-bounded slivers along the Norumbega fault system in eastern Maine (Wang and Ludman 2003). In adjacent New Brunswick, rocks of early Namurian age are represented by the upper portions of the Mabou Group in the Maritimes Basin (St. Peter and Johnson 2009). These rocks are dominated by fine-grained terrestrial clastic rocks and the subordinate aforementioned alkaline volcanic rocks of the Cumberland Hill Formation (ca. 335 Ma; Gray et al. 2010). In southern New England, Carboniferous strata are preserved in the Narragansett and Norfolk, and Worcester basins of Rhode Island and Massachusetts (Hermes et al. 1994; Zen et al. 1983). Rocks of demonstrable Namurian/Morrowan age in these basins are unknown; the basin fill consists, instead, of younger nonmarine clastic sedimentary rocks of middle to late Pennsylvanian age (Skehan et al. 1979; Murray et al. 2004).
Regional tectonic significance
28 The early Pennsylvanian age of the Lithchfield pluton corresponds to a time in the northern Appalachians that was dominated by transcurrent tectonics (Bradley 1982; Ludman and West 1999; Murphy et al. 2011; Waldron et al. 2015). Although the stratified and igneous rock record of this activity is largely lacking in Maine, the adjacent regions of Atlantic Canada (Maritimes Basin) and coastal southern New England (Narragansett Basin) contain thick successions of largely non-marine Carboniferous strata that were deposited in large transtensional pull-apart basins. Although generally 20 to 40 million years older than the Litchfield pluton, alkalic igneous rocks in these basins have been interpreted to have been generated through localized decompression melting in association with the transcurrent tectonic origins of these basins (Pe-Piper and Piper 1998; LaFleche et al. 1998; Thompson and Hermes, 2003).
29 Immediately east of the Litchfield pluton in south-central and southwestern Maine (Fig. 1), Carboniferous right-lateral strike-slip faulting associated with the Norumbega fault system is pervasive (West and Hubbard 1997; Swanson 1999; West 1999). We propose that a likely northern Appalachian tectonic equivalent for the origins of the alkalic magmatism at Litchfield, Maine can be found in the Cobequid Highlands of Nova Scotia. In this area, Late Devonian to early Carboniferous alkalic magmatism has been attributed to local extension along portions of the right-lateral Cobequid-Chebabucto fault zone (Koukouvelas et al. 2002; Pe-Piper et al. 2004). Park et al. (2014) suggested a similar origin for a recently identified assemblage of Late Devonian–early Carboniferous alkalic rocks in the Partridge Island block in coastal New Brunswick. Papoutsa et al. (2015) proposed a model for the Late Devonian-Carboniferous alkalic magmatism in the Cobequid Highlands that involves the emplacement of mafic melts in the lower crust due to extension, followed by partial melting of surrounding crustal rocks. The resulting alkalic felsic melts then ascended to higher crustal levels via faults associated with the Cobequid fault zone (Park et al. 2014).
30 Based on the established transcurrent tectonic setting present along the eastern margin of the northern Appalachians in Carboniferous time, we believe the most plausible triggering mechanism for the generation of the ca. 321 Ma alkalic plutonic rocks near Litchfield, Maine is deep-level extension associated with the regionally extensive Norumbega fault system. Although the Litchfield pluton is located approximately 15 km northwest of the Norumbega fault system sensu stricto, dextral shear deformation has been documented along strike to the northeast (Short and Johnson 2006), and extends west of the more prominent mapped faults of the system. The large Carboniferous pull-apart basins in adjacent areas of southern New England and New Brunswick, which include some alkalic igneous rocks, are more obvious manifestations of this period of transcurrent tectonism in the northern Appalachians. The record of this tectonism in Maine is limited to faulting associated with the Norumbega fault system and, we believe, alkalic magmatism near Litchfield.
CONCLUSIONS
- Recent detailed mapping and the results of this study confirm the earlier work of Barker (1965) and show that the 7 km2 Litchfield pluton in south-central Maine is a composite strongly alkalic intrusion that cuts previously deformed and metamorphosed Silurian turbidites of the Central Maine basin. Rock types within the pluton include Na-amphibole and pyroxene bearing syenite, biotite syenite, and nepheline syenite that includes the type variety of “litchfieldite” that is found in many petrologic collections (coarse-grained, nepheline syenite containing cancrinite, sodalite, and lepiodomelane).
- A new U-Pb zircon age of 321 ± 2 Ma from the nepheline syenite is interpreted to date igneous crystallization of the pluton. A 40Ar/39Ar biotite age of 239 ± 1 Ma is similar to previously published mica ages from surrounding country rocks and indicates the region cooled below approximately 300°C in the Early Triassic.
- Whole rock geochemistry of a select number of samples from the pluton reveal alkalic, silica-undersaturated, metaluminous compositions that are consistent with fractionation of an initial alkalic basalt parental magma. Geochemical signatures are consistent with magma generation in an anorogenic tectonic setting.
- The age and geochemical characteristics of the alkalic rocks near Litchfield, Maine are consistent with the generation of a small volume of alkalic magma beneath south-central Maine during a period of Carboniferous transcurrent tectonism in the northern Appalachian orogen.
Funding for this work was provided by the Maine Geological Survey through the STATEMAP program, and by the Middlebury College Geology Department. Evan Ellenberger is thanked for help in the field, Andrew McCauley for his part in the U-Pb SHRIMP analyses, and Mick Kunk for completing the 40Ar/39Ar analyses. We thank reviewers Joe Whalen, Marti Miller, and Dave Gibson, and journal editor Sandra Barr for their helpful comments and suggestions which led to significant improvements in the manuscript. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the United States Government.
APPENDIX A. Litchfield Pluton sample locations and general descriptions (Locations in UTM grid coordinates, Zone 19T)
- P-281: (Easting 0428892, Northing 4894500) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular, medium to coarse grained, biotite (<5%) nepheline syenite.
- P-304: (Easting 0428235, Northing 4895224) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular medium grained, biotite (~ 12%), syenite.
- P-305: (Easting 0428293, Northing 4895659) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular, medium to coarse grained, magnetite-bearing, biotite (< 5%) nepheline syenite.
- P-310: (Easting 428849, Northing 4896313) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular, medium grained, aegerine and riebeckite-bearing (~ 5%), syenite.
- P-333: (Easting 0426665, Northing 4893736) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular, medium to coarse grained, cancrinite-bearing (< 5%), biotite (~ 6%), nepheline syenite.
- P-603: (Easting 0426452, Northing 4894310) Light grey, hypidiomorphic-granular, coarse-grained with biotite schlieren, biotite (~ 12%), cancrinite (~ 15%), nepheline syenite.